1. Geneology
2. Gist
3. Summary
4. Detailed View
5.Detailed View in Tamil ( தமிழில் விரிவான உள்ளடக்கம் )
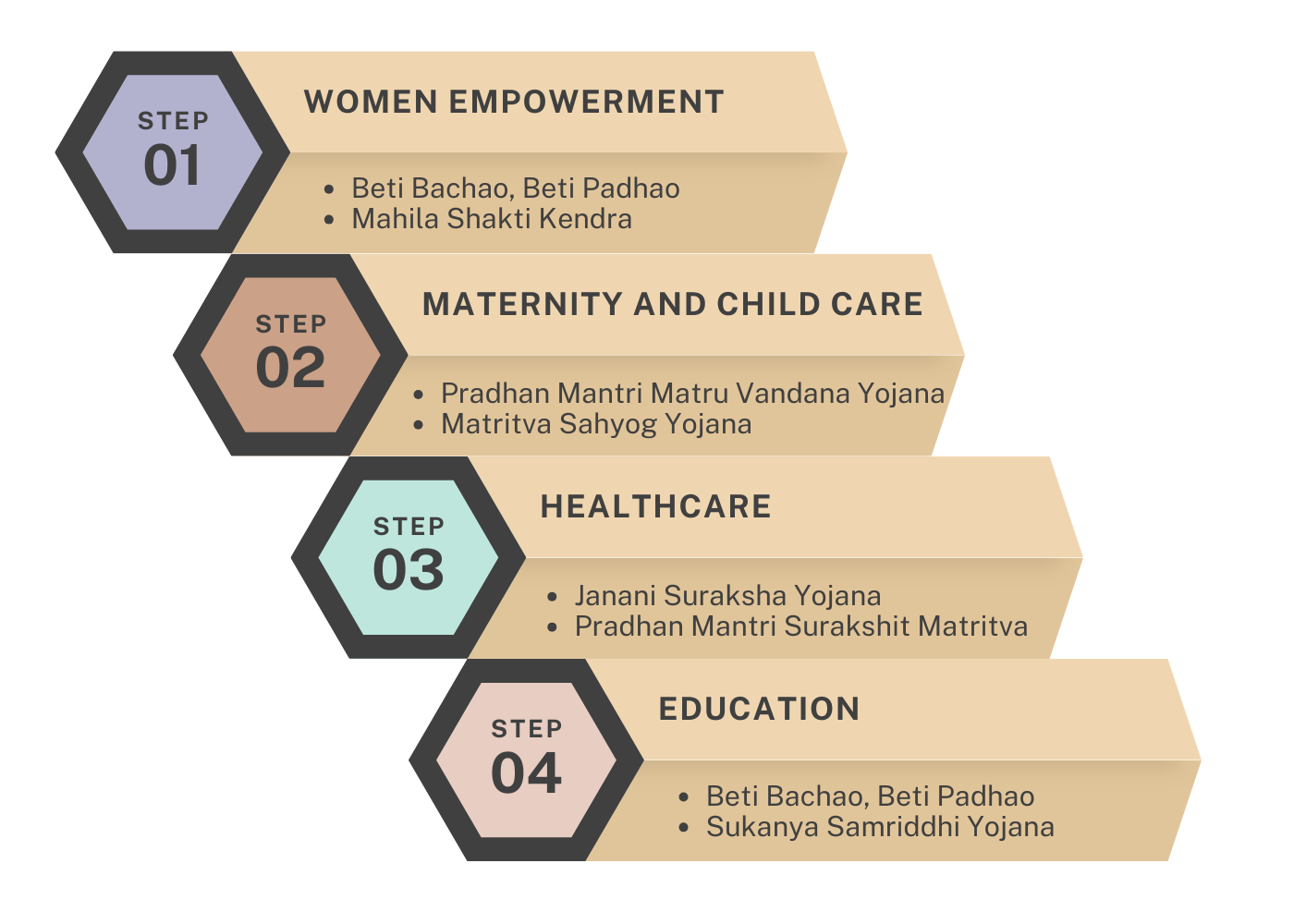
India recognizes the crucial role of women and children in its development and has implemented numerous welfare schemes to address their needs. Here's a gist
Key Schemes
• Focusing on different stages of life: Schemes support women and children from pre-natal care to old age, covering diverse needs like health, education, nutrition, and protection.
• Major Initiatives:
• Pre-natal and Maternal Health: PM Matru Vandana Yojana, ICDS (Anganwadi program), Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (Ayushman Bharat).
• Child Health and Nutrition: National Immunization Programme, Mid-Day Meal Scheme, POSHAN Abhiyaan.
• Girl Child Education: Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, RTE Act, Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya.
• Women's Empowerment: Mahila Shakti Kendra, Ujjwala Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (housing).
• Protection: Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, Juvenile Justice Act, One Stop Centres.
Significance
• Improve health and well-being: Reduced maternal mortality, child malnutrition, and increased access to healthcare.
• Promote education and empowerment: Increased literacy rates, especially among girls, and enhanced economic opportunities for women.
• Reduce vulnerabilities: Protection from exploitation, violence, and trafficking.
• Contribute to long-term development: Empowered women and healthy children contribute to a more equitable and prosperous society.
Challenges
• Resource limitations: Effective implementation requires adequate funding, which can be a constraint.
• Targeting and leakages: Ensuring benefits reach intended beneficiaries efficiently and without corruption remains a challenge.
• Awareness and access: Reaching marginalized communities and raising awareness about schemes are crucial.
• Sustainability: Long-term impact requires addressing underlying gender inequalities and societal biases.
Overall
• Welfare schemes represent a significant effort to address the needs of women and children in India.
• Continued efforts are needed to overcome challenges, improve implementation, and ensure schemes reach and empower their intended beneficiaries.
The welfare schemes for women and children in Indian polity and governance aim to address the multifaceted challenges faced by these vulnerable groups. Through initiatives such as the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY), and Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP), the government strives to improve nutrition, healthcare, education, and protection for women and children. Implementation involves a multi-tiered approach, with central, state, and local authorities working in tandem with grassroots-level institutions and NGOs. Despite progress, challenges such as gender disparities, health and nutrition issues, education barriers, violence, and data limitations persist. Overcoming these challenges requires sustained efforts, collaboration, and community engagement to ensure the holistic well-being and empowerment of women and children across India.
Introduction
In India, ensuring the welfare of women and children is a critical aspect of governance due to their vulnerability and the historical marginalization they have faced. Over the years, the government has implemented various schemes and programs to address their needs and uplift their socio-economic status. These initiatives span across healthcare, education, nutrition, protection, and empowerment sectors. The welfare schemes for women and children are designed to tackle issues such as maternal mortality, child malnutrition, gender inequality, access to education, child labor, and violence against women and children.
Historical Context
The focus on women and children's welfare in India can be traced back to various socio-political movements and policy frameworks initiated post-independence. The Constitution of India guarantees equality and freedom from discrimination on the basis of gender and mandates the state to ensure the welfare of children. Additionally, India is a signatory to international conventions like the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW), which have influenced policy formulation in this domain
Major Welfare Schemes
1. Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
• Launched in 1975, ICDS is one of the world's largest and most unique programs for early childhood care and development.
• It aims to provide health, nutrition, and pre-school education to children under 6 years of age, as well as pregnant and lactating mothers.
• Services under ICDS include supplementary nutrition, immunization, health check-ups, referral services, and early childhood education.
2. Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
• PMMVY, launched in 2017, aims to provide financial assistance to pregnant and lactating mothers to compensate for wage loss and ensure proper nutrition during pregnancy and lactation.
• It provides a cash incentive of Rs. 5,000 in three installments for the first living child.
3. Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP)
• Launched in 2015, this initiative focuses on addressing the declining child sex ratio and promoting the education of girls.
• It includes awareness campaigns, advocacy efforts, and financial incentives for the girl child's education.
4. National Nutrition Mission (POSHAN Abhiyaan)
• Launched in 2018, POSHAN Abhiyaan aims to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
• It focuses on reducing child malnutrition through a convergence of inter-sectoral actions, including health, education, water, sanitation, and women's empowerment.
5. Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
• This scheme, launched in 2015, encourages parents to save for the future education and marriage expenses of their girl child.
• It offers a higher interest rate and tax benefits, making it an attractive savings option for families.
6. Mahila Shakti Kendra (MSK)
• Launched as part of the Umbrella Scheme for Protection and Empowerment of Women, MSK aims to empower rural women through community participation.
• It provides skill development, capacity building, awareness generation, and support services for women's economic and social empowerment.
7. National Creche Scheme
• This scheme provides daycare facilities for children of working mothers in the age group of 6 months to 6 years.
• It aims to ensure the safety, health, and overall development of children while their mothers are at work.
8. Swadhar Greh Scheme
• Swadhar Greh provides temporary shelter, food, counseling, and rehabilitation services to women in difficult circumstances, such as victims of violence, trafficking, or destitution.
• It aims to provide a supportive environment for women to regain their self-confidence and become self-reliant.
Implementation Mechanisms
These welfare schemes are implemented through a multi-tiered governance structure involving central, state, and local authorities. The Ministry of Women and Child Development at the central level formulates policies, provides guidelines, allocates funds, and monitors the implementation of schemes. At the state level, respective departments are responsible for executing these schemes, adapting them to local needs, and ensuring effective delivery of services. Furthermore, grassroots-level institutions such as Anganwadi centers, self-help groups, panchayats, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in reaching out to beneficiaries, raising awareness, and facilitating community participation.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the existence of various welfare schemes, several challenges persist in ensuring the holistic welfare of women and children in India:
1. Inadequate Implementation
Limited infrastructure, human resources, and capacity constraints often hinder the effective implementation of welfare schemes, particularly in remote and underserved areas
2. Gender Disparities
Deep-rooted socio-cultural norms and practices perpetuate gender disparities, leading to differential access to resources, opportunities, and decision-making power for women and girls.
3. Nutrition and Health
Despite efforts to address malnutrition and maternal health, India continues to grapple with high rates of child malnutrition, maternal mortality, and inadequate healthcare facilities, especially in rural and tribal areas.
4. Education and Child Labor
While strides have been made in promoting girls education, challenges such as school dropout rates, child labor, and lack of quality education remain significant barriers to realizing children's rights.
5. Violence and Trafficking
Women and children are vulnerable to various forms of violence, including domestic violence, sexual abuse, trafficking, and exploitation. Despite legal provisions and support mechanisms, underreporting, stigma, and impunity persist.
6. Data and Monitoring
Inadequate data collection, monitoring mechanisms, and outcome evaluation pose challenges in assessing the impact of welfare schemes and addressing gaps in service delivery.
Conclusion
Welfare schemes for women and children in Indian polity and governance reflect the government's commitment to safeguarding their rights, promoting their well-being, and addressing socio-economic disparities. While significant progress has been made in expanding access to essential services and enhancing opportunities for empowerment, persistent challenges underscore the need for sustained efforts, multi-sectoral collaboration, and community engagement. By addressing systemic barriers, strengthening implementation mechanisms, and prioritizing the most vulnerable populations, India can strive towards achieving inclusive and sustainable development for all its citizens, particularly its women and children.
அறிமுகம்
இந்தியாவில், பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளின் நலனை உறுதி செய்வது நிர்வாகத்தின் ஒரு முக்கியமான அம்சமாகும், ஏனெனில் அவர்களின் பாதிப்பு மற்றும் அவர்கள் எதிர்கொண்ட வரலாற்று ஓரங்கட்டப்படுதல். பல ஆண்டுகளாக, அவர்களின் தேவைகளை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதற்கும் அவர்களின் சமூக-பொருளாதார நிலையை மேம்படுத்துவதற்கும் அரசாங்கம் பல்வேறு திட்டங்கள் மற்றும் திட்டங்களை செயல்படுத்தியுள்ளது. இந்த முயற்சிகள் சுகாதாரம், கல்வி, ஊட்டச்சத்து, பாதுகாப்பு மற்றும் அதிகாரமளித்தல் துறைகளில் பரவியுள்ளன. பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளுக்கான நலத்திட்டங்கள் தாய்வழி இறப்பு, குழந்தை ஊட்டச்சத்து குறைபாடு, பாலின சமத்துவமின்மை, கல்விக்கான அணுகல், குழந்தைத் தொழிலாளர் மற்றும் பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளுக்கு எதிரான வன்முறை போன்ற பிரச்சினைகளைச் சமாளிக்க வடிவமைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன.
வரலாற்று சூழல்
இந்தியாவில் பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகள் நலனில் கவனம் செலுத்துவது சுதந்திரத்திற்குப் பிறகு தொடங்கப்பட்ட பல்வேறு சமூக-அரசியல் இயக்கங்கள் மற்றும் கொள்கை கட்டமைப்புகளில் காணப்படுகிறது. இந்திய அரசியலமைப்புச் சட்டம் சமத்துவம் மற்றும் பாலின அடிப்படையிலான பாகுபாட்டிலிருந்து சுதந்திரத்திற்கு உத்தரவாதம் அளிக்கிறது மற்றும் குழந்தைகளின் நலனை உறுதி செய்ய அரசை கட்டாயப்படுத்துகிறது. கூடுதலாக, குழந்தைகளின் உரிமைகள் பற்றிய மாநாடு (CRC) மற்றும் பெண்களுக்கு எதிரான அனைத்து வகையான பாகுபாடுகளையும் ஒழிப்பதற்கான மாநாடு (CEDAW) போன்ற சர்வதேச மாநாடுகளுக்கு இந்தியா கையொப்பமிட்டுள்ளது
முக்கிய நலத்திட்டங்கள்
1. ஒருங்கிணைந்த குழந்தை மேம்பாட்டு சேவைகள் (ICDS)
• 1975 இல் தொடங்கப்பட்டது, ஐ.சி.டி.எஸ் என்பது குழந்தை பருவ பராமரிப்பு மற்றும் மேம்பாட்டிற்கான உலகின் மிகப்பெரிய மற்றும் மிகவும் தனித்துவமான திட்டங்களில் ஒன்றாகும்.
• இது 6 வயதிற்குட்பட்ட குழந்தைகளுக்கும், கர்ப்பிணி மற்றும் பாலூட்டும் தாய்மார்களுக்கும் சுகாதாரம், ஊட்டச்சத்து மற்றும் முன்பள்ளி கல்வியை வழங்குவதை நோக்கமாகக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
• ஐ.சி.டி.எஸ்ஸின் கீழ் உள்ள சேவைகளில் துணை ஊட்டச்சத்து, நோய்த்தடுப்பு, சுகாதார பரிசோதனைகள், பரிந்துரை சேவைகள் மற்றும் குழந்தை பருவ கல்வி ஆகியவை அடங்கும்.
2. Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
• PMMVY, 2017 இல் தொடங்கப்பட்டது, கர்ப்பிணி மற்றும் பாலூட்டும் தாய்மார்களுக்கு ஊதிய இழப்பை ஈடுசெய்வதற்கும், கர்ப்பம் மற்றும் பாலூட்டும் போது சரியான ஊட்டச்சத்தை உறுதி செய்வதற்கும் நிதி உதவி வழங்குவதை நோக்கமாகக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
• உயிருள்ள முதல் குழந்தைக்கு மூன்று தவணைகளில் ரூ.5,000 ஊக்கத்தொகை வழங்கப்படுகிறது.
3. பெண் குழந்தையை பாதுகாப்போம் பெண் குழந்தைக்கு கற்பிப்போம் (BBBP)
• 2015 இல் தொடங்கப்பட்ட இந்த முயற்சி, குறைந்து வரும் குழந்தை பாலின விகிதத்தை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதிலும், சிறுமிகளின் கல்வியை மேம்படுத்துவதிலும் கவனம் செலுத்துகிறது.
• இதில் விழிப்புணர்வு பிரச்சாரங்கள், வக்காலத்து முயற்சிகள் மற்றும் பெண் குழந்தையின் கல்விக்கான நிதி சலுகைகள் ஆகியவை அடங்கும்.
4. தேசிய ஊட்டச்சத்து இயக்கம் (போஷன் அபியான்)
• 2018 இல் தொடங்கப்பட்டது, போஷன் அபியான் குழந்தைகள், கர்ப்பிணிப் பெண்கள் மற்றும் பாலூட்டும் தாய்மார்களுக்கான ஊட்டச்சத்து விளைவுகளை மேம்படுத்துவதை நோக்கமாகக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
• சுகாதாரம், கல்வி, நீர், சுகாதாரம் மற்றும் பெண்கள் அதிகாரமளித்தல் உள்ளிட்ட துறைகளுக்கு இடையேயான நடவடிக்கைகளின் ஒருங்கிணைப்பின் மூலம் குழந்தை ஊட்டச்சத்து குறைபாட்டைக் குறைப்பதில் இது கவனம் செலுத்துகிறது.
5. சுகன்யா சம்ரிதி யோஜனா
• 2015 இல் தொடங்கப்பட்ட இந்தத் திட்டம், பெற்றோர்கள் தங்கள் பெண் குழந்தையின் எதிர்கால கல்வி மற்றும் திருமணச் செலவுகளைச் சேமிக்க ஊக்குவிக்கிறது.
• இது அதிக வட்டி விகிதம் மற்றும் வரி சலுகைகளை வழங்குகிறது, இது குடும்பங்களுக்கு கவர்ச்சிகரமான சேமிப்பு விருப்பமாக அமைகிறது.
6. மகிளா சக்தி கேந்திரா (MSK)
• பெண்களின் பாதுகாப்பு மற்றும் அதிகாரமளித்தலுக்கான குடை திட்டத்தின் ஒரு பகுதியாக தொடங்கப்பட்ட எம்.எஸ்.கே, சமூக பங்களிப்பின் மூலம் கிராமப்புற பெண்களுக்கு அதிகாரம் அளிப்பதை நோக்கமாகக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
• இது திறன் மேம்பாடு, திறன் மேம்பாடு, விழிப்புணர்வு உருவாக்கம் மற்றும் பெண்களின் பொருளாதார மற்றும் சமூக அதிகாரமளித்தலுக்கான ஆதரவு சேவைகளை வழங்குகிறது.
7. தேசிய குழந்தைகள் காப்பகத் திட்டம்
• இத்திட்டம் 6 மாதம் முதல் 6 வயது வரை உள்ள பணிபுரியும் தாய்மார்களின் குழந்தைகளுக்கு பகல் நேர பராமரிப்பு வசதிகளை வழங்குகிறது.
• தாய்மார்கள் பணியில் இருக்கும்போது குழந்தைகளின் பாதுகாப்பு, ஆரோக்கியம் மற்றும் ஒட்டுமொத்த வளர்ச்சியை உறுதி செய்வதை இது நோக்கமாகக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
8. ஸ்வதார் கிரே திட்டம்
• வன்முறை, கடத்தல் அல்லது ஆதரவற்ற நிலை போன்ற கடினமான சூழ்நிலைகளில் உள்ள பெண்களுக்கு தற்காலிக தங்குமிடம், உணவு, ஆலோசனை மற்றும் மறுவாழ்வு சேவைகளை Swadhar Greh வழங்குகிறது.
• பெண்கள் தங்கள் தன்னம்பிக்கையை மீண்டும் பெறுவதற்கும் தன்னம்பிக்கை அடைவதற்கும் ஆதரவான சூழலை வழங்குவதை இது நோக்கமாகக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
செயல்படுத்தல் வழிமுறைகள்
இந்த நலத்திட்டங்கள் மத்திய, மாநில மற்றும் உள்ளூர் அதிகாரிகளை உள்ளடக்கிய பல அடுக்கு ஆளுகை கட்டமைப்பின் மூலம் செயல்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன. மத்திய அளவில் பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகள் மேம்பாட்டு அமைச்சகம் கொள்கைகளை வகுத்தல், வழிகாட்டுதல்களை வழங்குதல், நிதி ஒதுக்கீடு செய்தல் மற்றும் திட்டங்கள் செயல்படுத்தப்படுவதை கண்காணித்தல் போன்ற பணிகளை மேற்கொள்கிறது. மாநில அளவில், இந்தத் திட்டங்களை செயல்படுத்துவதற்கும், உள்ளூர் தேவைகளுக்கு ஏற்ப அவற்றை மாற்றியமைப்பதற்கும், சேவைகளை திறம்பட வழங்குவதை உறுதி செய்வதற்கும் அந்தந்த துறைகள் பொறுப்பாகும். மேலும், அங்கன்வாடி மையங்கள், சுய உதவிக் குழுக்கள், பஞ்சாயத்துகள் மற்றும் அரசு சாரா நிறுவனங்கள் (என்.ஜி.ஓ) போன்ற அடிமட்ட அளவிலான நிறுவனங்கள் பயனாளிகளை அணுகுவதற்கும், விழிப்புணர்வை ஏற்படுத்துவதற்கும், சமூக பங்களிப்பை எளிதாக்குவதற்கும் முக்கிய பங்கு வகிக்கின்றன.
சவால்கள் மற்றும் வரம்புகள்
பல்வேறு நலத்திட்டங்கள் இருந்தபோதிலும், இந்தியாவில் பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளின் முழுமையான நலனை உறுதி செய்வதில் பல சவால்கள் உள்ளன:
1. போதிய அமலாக்கம்
வரையறுக்கப்பட்ட உள்கட்டமைப்பு, மனித வளங்கள் மற்றும் திறன் கட்டுப்பாடுகள் பெரும்பாலும் நலத்திட்டங்களை திறம்பட செயல்படுத்துவதைத் தடுக்கின்றன, குறிப்பாக தொலைதூர மற்றும் பின்தங்கிய பகுதிகளில்
2. பாலின ஏற்றத்தாழ்வுகள்
ஆழமாக வேரூன்றிய சமூக-கலாச்சார விதிமுறைகள் மற்றும் நடைமுறைகள் பாலின ஏற்றத்தாழ்வுகளை நிலைநிறுத்துகின்றன, இது பெண்கள் மற்றும் சிறுமிகளுக்கான வளங்கள், வாய்ப்புகள் மற்றும் முடிவெடுக்கும் அதிகாரத்திற்கான மாறுபட்ட அணுகலுக்கு வழிவகுக்கிறது.
3. ஊட்டச்சத்து மற்றும் சுகாதாரம்
ஊட்டச்சத்து குறைபாடு மற்றும் தாய்வழி ஆரோக்கியத்தை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதற்கான முயற்சிகள் இருந்தபோதிலும், குழந்தை ஊட்டச்சத்து குறைபாடு, தாய்வழி இறப்பு மற்றும் போதிய சுகாதார வசதிகள், குறிப்பாக கிராமப்புற மற்றும் பழங்குடியினர் பகுதிகளில் அதிக விகிதங்களை இந்தியா தொடர்ந்து எதிர்கொள்கிறது.
4. கல்வி மற்றும் குழந்தைத் தொழிலாளர்
சிறுமிகளின் கல்வியை மேம்படுத்துவதில் முன்னேற்றம் ஏற்பட்டாலும், பள்ளி இடைநிற்றல் விகிதம், குழந்தைத் தொழிலாளர் மற்றும் தரமான கல்வி இல்லாமை போன்ற சவால்கள் குழந்தைகளின் உரிமைகளை உணர குறிப்பிடத்தக்க தடைகளாக உள்ளன.
5. வன்முறை மற்றும் கடத்தல்
குடும்ப வன்முறை, பாலியல் துஷ்பிரயோகம், கடத்தல் மற்றும் சுரண்டல் உள்ளிட்ட பல்வேறு வகையான வன்முறைகளுக்கு பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகள் பாதிக்கப்படுகின்றனர். சட்ட விதிகள் மற்றும் ஆதரவு வழிமுறைகள் இருந்தபோதிலும், குறைத்து அறிக்கை, களங்கம் மற்றும் தண்டனையிலிருந்து விலக்களிப்பு ஆகியவை தொடர்கின்றன.
6. தரவு மற்றும் கண்காணிப்பு
போதிய தரவு சேகரிப்பு, கண்காணிப்பு வழிமுறைகள் மற்றும் விளைவு மதிப்பீடு ஆகியவை நலத்திட்டங்களின் தாக்கத்தை மதிப்பிடுவதிலும், சேவை வழங்கலில் உள்ள இடைவெளிகளை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதிலும் சவால்களை ஏற்படுத்துகின்றன.
முடிவுரை
இந்திய அரசியல் மற்றும் ஆட்சியில் பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளுக்கான நலத்திட்டங்கள் அவர்களின் உரிமைகளைப் பாதுகாப்பதற்கும், அவர்களின் நல்வாழ்வை மேம்படுத்துவதற்கும், சமூக-பொருளாதார ஏற்றத்தாழ்வுகளை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதற்கும் அரசாங்கத்தின் உறுதிப்பாட்டை பிரதிபலிக்கின்றன. அத்தியாவசிய சேவைகளுக்கான அணுகலை விரிவுபடுத்துதல் மற்றும் அதிகாரமளித்தலுக்கான வாய்ப்புகளை மேம்படுத்துதல் ஆகியவற்றில் குறிப்பிடத்தக்க முன்னேற்றம் ஏற்பட்டுள்ள நிலையில், தொடர்ச்சியான சவால்கள் நீடித்த முயற்சிகள், பல துறை ஒத்துழைப்பு மற்றும் சமூக ஈடுபாடு ஆகியவற்றின் அவசியத்தை அடிக்கோடிட்டுக் காட்டுகின்றன. முறையான தடைகளை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதன் மூலமும், அமலாக்க வழிமுறைகளை வலுப்படுத்துவதன் மூலமும், மிகவும் பாதிக்கப்படக்கூடிய மக்களுக்கு முன்னுரிமை அளிப்பதன் மூலமும், இந்தியா தனது அனைத்து குடிமக்களுக்கும், குறிப்பாக அதன் பெண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளுக்கு உள்ளடக்கிய மற்றும் நிலையான வளர்ச்சியை அடைவதற்கு பாடுபட முடியும்.